Let’s take a look at what Cisco UCS Manager is, and what it does for the Cisco UCS platform.
What Is Cisco UCS Manager?
Cisco UCS Manager is the element manager for the Cisco UCS platform, with one small caveat, you must be using the Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects.
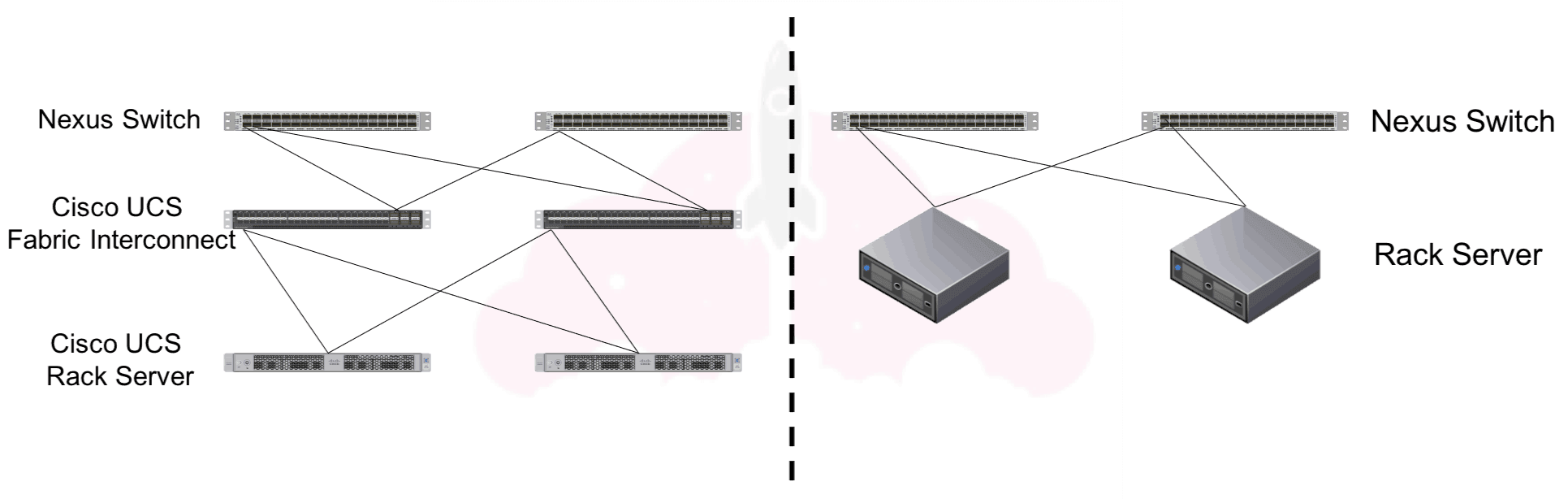
As discussed in my Introduction to Cisco UCS Architecture, Cisco UCS comes in two main flavors: managed and unmanaged. The difference between these flavors of Cisco UCS are the including of Cisco Fabric Interconnects and the use of UCS Manager, as illustrated here:
In this article, we will be talking about the configuration on the left, or a managed Cisco UCS configuration.
Cisco UCS Manager lives on the Cisco Fabric Interconnects, which are the brains of a Cisco UCS deployment. This is why you would not use Cisco UCS manager without the Cisco Fabric Interconnects.
What Does Cisco UCS Manager Do?
The short answer is everything! You will use Cisco UCS manager for the initial setup, as well as ongoing management of your Cisco UCS deployment. You will configure things like:
- Uplink from Fabric Interconnect to Cisco Nexus Switch
- VLANs
- Service Profiles for Servers
- Syslog
- Authentication
Pretty much anything you can think of will be configured from UCS Manager. Remember, the Cisco Fabric Interconnects are the brains of your Cisco UCS environment, and UCS Manager lives there.
When Cisco adds new functionality to the Cisco UCS platform, it usually comes in the form of a Cisco UCS Manager update. Besides adding new features, Cisco UCS Manager updates are often also released to support new hardware platforms. For example, you can see the progression of Cisco UCS Manager features in some of these articles:
Cisco UCS Service Profiles
Cisco UCS Service Profiles are the most magical part of the Cisco UCS platform. A Cisco UCS service profile allows you to abstract the hardware personality of a Cisco UCS Server.
You can create templates for configuration aspects such as storage and networking, then add them to a service profile. A service profile is then attached to a Cisco UCS server, and it assumes the personality assigned to it.
For example, I may have a server I need to configure with NFS IP based storage, and eight vNICs, or I may have a server I need to configure with iSCSI storage and four vNICs. Or perhaps I have not decided which configuration is best for my environment.
The service profile, or hardware personality of a Cisco UCS server , can be changed with a simple reboot. This means you can be running ESXi, reboot with a new service profile, and then be running Hyper-V (yes, I have done this!) with whatever networking and storage options you would like.
The best part about service profiles is that you can configure them once, and create multiple copies of a service to assign to servers – no need to create custom configurations for each and every server.
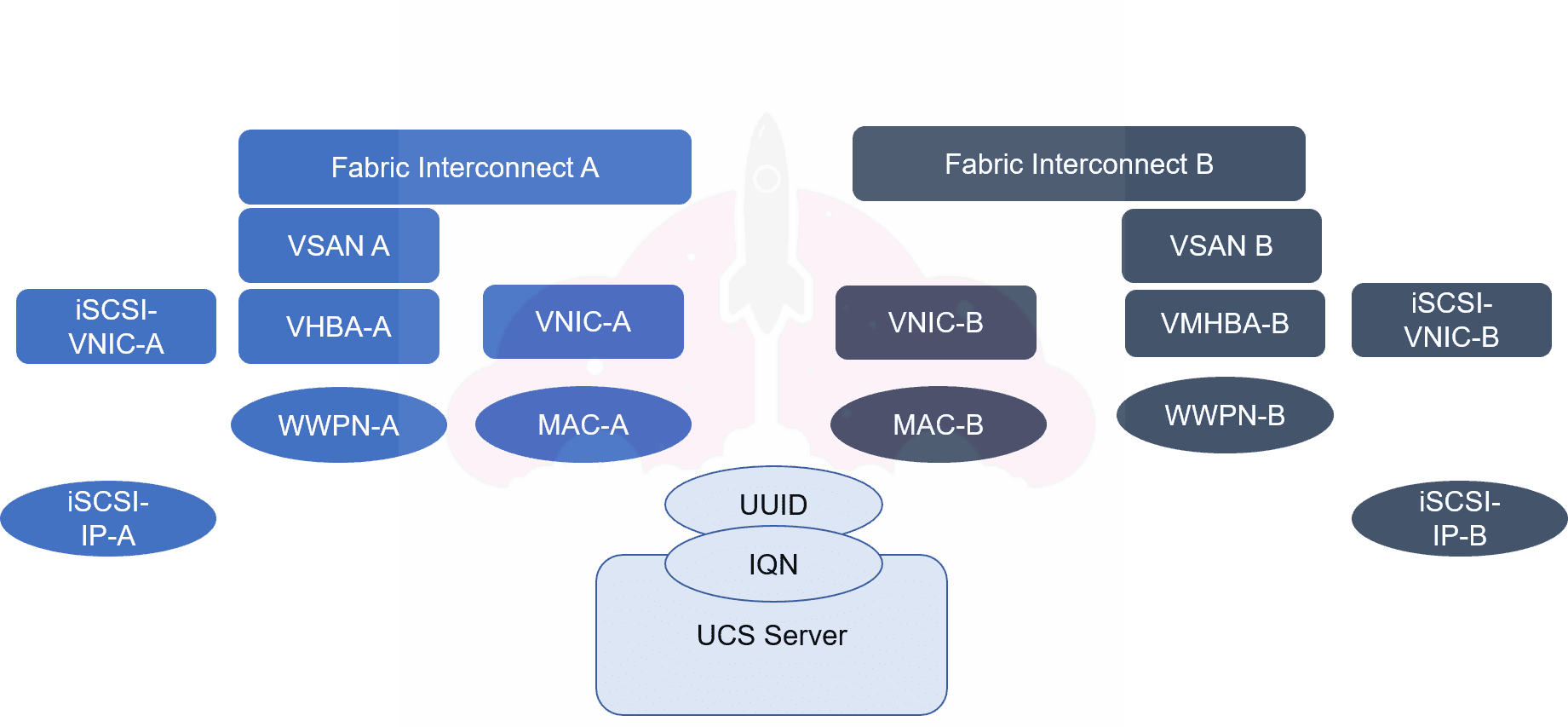
Now, let’s take a look at some possible components of a service profile:
Of course, we have our Cisco Fabric interconnects, where Cisco UCS Manager is installed. We always deploy two Fabric Interconnects for redundancy, and as you can see our service profile has identical components on each fabric to ensure availability in the case of a Fabric Interconnect failure, or to allow maintenance, and Cisco UCS Manager upgrades on the Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect.
The round circles represent pools assets assigned by pools. Pools are a pre-configured range of attributes that will be assigned to your service profiles as they are crated. This is one reason why service profiles are set it and forget it, I just need to set a range and amount of UUIDs, IQNs, IPs, MACs, or WWPNs, and they will be automatically assigned at deployment time.
The rectangles represent other configuration attributes that must be configured, such as the numbers and properties of a VNIC, HBA, etc. These are a product of the Cisco VIC or Cisco Virtual Interface Card. The Cisco VIC allows you to create virtual network or storage adapters to meet your configuration requirement.
All of these attributes make up your server’s service profile, or hardware personality, and remember, you can switch between service profiles as you need to. This is especially powerful in test and development environments.
I do not know if people would consider this a good statistic or not, but I know I can go from a blank Cisco UCS system to running ESXi in approximately four hours. To me that is pretty cool, and a testament to how powerful and easy to use Cisco UCS Manager is.
Cisco UCS Manager Configuration Options
Currently, Cisco UCS Manager is accessed via a HTML 5 web client. Previously, it was a java based client. You can read more about the difference in Cisco UCS clients here. While Cisco UCS Manager was always easy to use, the introduction of the HTML5 client made it even quicker and more user friendly.
You may configure your Cisco UCS environment using the HTML5 web client, or, if you are a PowerShell person, you can use the Cisco UCS PowerTool.
You can also backup an existing UCS Manager configuration and import it into another UCS Manager system. This is very handy when you have similar configurations for different UCS domains.
Cisco UCS Manager Creates a UCS Domain
I have just used the term UCS domain, and it is something you will come into contact with quite a bit when you are talking about Cisco UCS servers. A Cisco UCS domain is simply the Cisco UCS fabric interconnects, and the Cisco UCS servers attached to it.
As the Cisco UCS platform has evolved, the configuration maximums of a UCS domain have also evolved. Currently up to 20 Cisco UCS 5100 blade server chassis or 160 Cisco UCS servers are supported in a single UCS Domain.
Getting Your Hands on Cisco UCS Manager
The best way to see what Cisco UCS Manager is all about is to get your hands on it. Believe it or not, you do not have to have Cisco UCS hardware to get practical hands on experience with Cisco UCS Manager.
Enter the Cisco UCS Platform Emulator. You may also hear this referred to as the Cisco UCS Emulator or UCSPE. Cisco does offer a number of emulators for various products, and this one is specific to Cisco UCS.
Check out these helpful guides for working with the Cisco UCS Emulator:
- Setup and Use of the Cisco UCS Platform Emulator
- Tips and Tricks for Using the Cisco UCS Platform Emulator
- Updating Your UCS Platform Emulator
- Changing Fabric Interconnects on the UCS Platform Emulator
- Getting Started With Cisco UCS Platform Emulator Version 3.2(3ePE1)
These guides will have you working with Cisco UCS Manager in no time at all!
Other Cisco UCS Management Tools
Beyond Cisco UCS Manager, there are additional tools to mange a Cisco UCS environment. Below is a list of tools, and a brief description. Stay tuned for a deep dive on each one!
- Cisco Intersight. A cloud based option for Cisco UCS management, including Cisco HyperFlex.
- Cisco UCS Central. Allows management of up to 10,000 Cisco UCS servers across multiple UCS domains.
- Cisco UCS Director. Powerful management and automation for your Cisco UCS environment. Also gives you a great look at how resources are being utilized across your complete infrastructure.
- Cisco Integrated Management Controller. This is for unmanaged Cisco UCS environments without a Cisco Fabric Interconnect. Think of rack server based management tools like iLO and DRAC, but better.
- Cisco IMC Supervisor. Enhances management of unmanaged/stand alone Cisco UCS rack server deployments.
Cisco UCS Manager, The Brains of Cisco UCS
Cisco UCS Manager is easy to use, and a powerful tool for managing your Cisco UCS environment. Configure it once, set it, and forget it. It is also easy to add new configurations should your environment’s requirements change over time. You could make an argument that Cisco UCS servers are just like any other, but the real differentiation is Cisco UCS Manager and the other powerful management options.

Melissa is an Independent Technology Analyst & Content Creator, focused on IT infrastructure and information security. She is a VMware Certified Design Expert (VCDX-236) and has spent her career focused on the full IT infrastructure stack.