Let’s talk about recovery locations in Veeam Disaster Recovery Orchestrator. A recovery location is simply a logical grouping of the resources you are going to recover your VMs to.
It consists of a few items, vSphere hosts and clusters, storage, and any network mapping and re-IP rules to make sure we know exactly where we are going to recover to.
Let’s take a closer look at the types of recovery locations in Orchestrator.
Storage Recovery Locations (Storage Replication)
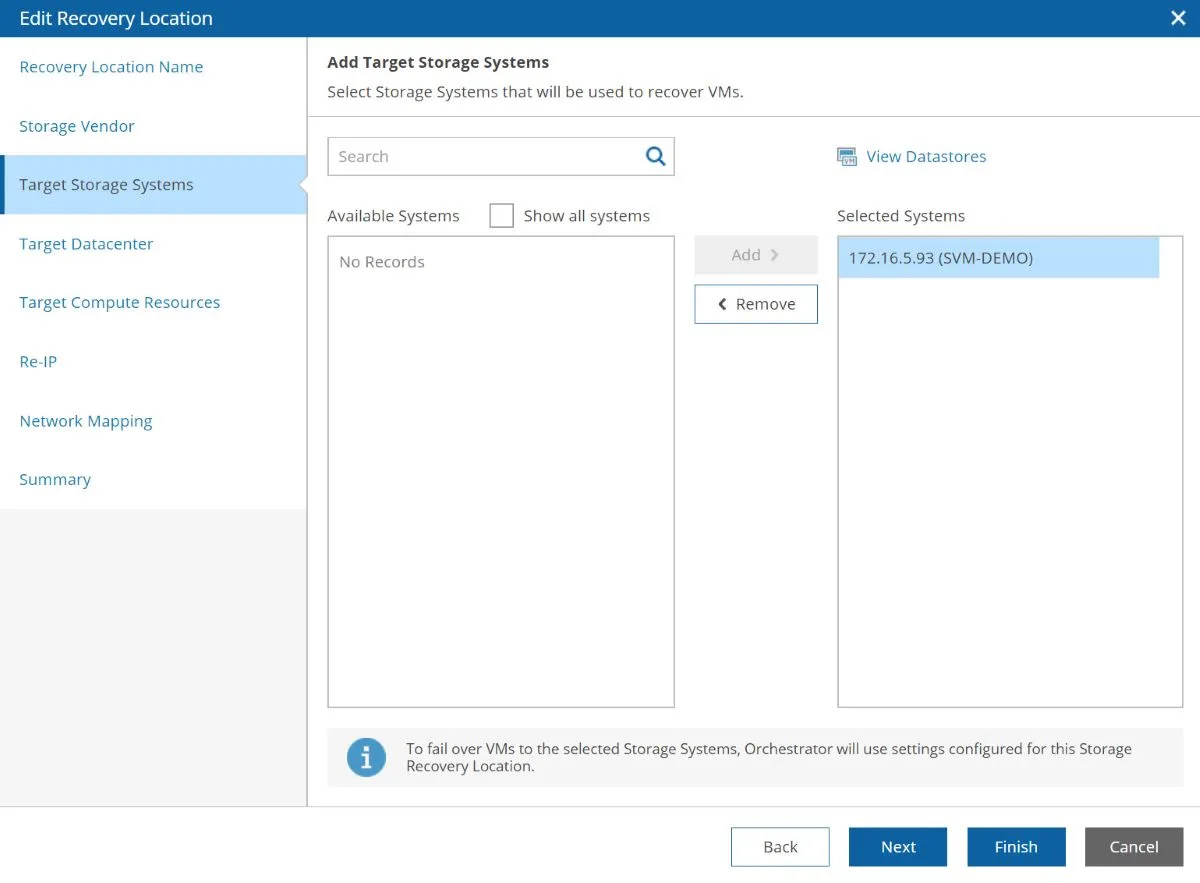
When you create a recovery location for a storage plan, you’ll be mapping in the storage array to your vSphere hosts and clusters, along with any network/IP rules.
Once you have recovery locations configured in this context, Orchestrator will automatically pick the best storage recovery location when you run a plan, since it understands the replication relationship between the storage arrays you have connected.
That’s it. It is very much set it and forget it.
Restore Recovery Locations (Restore from Backup)
When it comes to a restore recovery location you will use in conjunction with automatically restoring your backups, we have a few more options.
First, we need to decide if we would like to use Veeam VM instant VM recovery technology or not. That is a simple setting on the recovery location, and Orchestrator will always show us what we have chosen through the various screens in the UI.
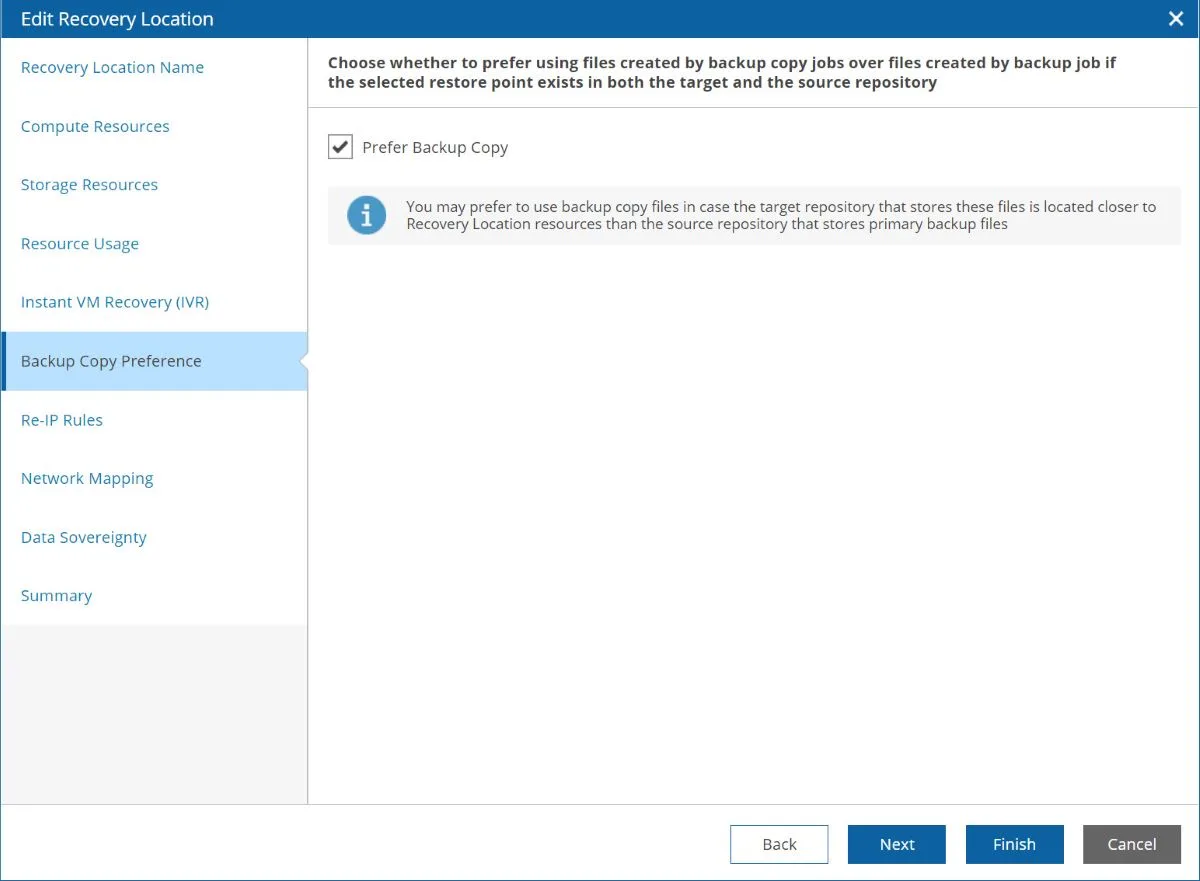
There is also the ability to leverage backup copies for recovery, which is key if you are leveraging backup copy jobs in your environment.
If you’re using backup copy jobs, this is an important setting for your recovery location, since we want to use the copy of the data that is closest to our vSphere environment for the fastest recovery.
This brings us to a special recovery location that you don’t need to configure, but you should be aware about.
Original VM Location
Out of the box, Orchestrator can recover VMs to the original location. This recovery location does not require any additional configuration, and is always available to restore plans.
Flexibility for Recovery
When it comes to restore plans, recovery locations can be changed at any time, in multiple ways. The plan can simply be edited, and the recovery location changed. When a readiness check runs, this is the recovery location that will be examined.
Recovery locations can also be changed during a disaster recovery test (DataLab test) and when a plan is launched in the event of a disaster.
It is a good idea to test your plans against each and every recovery location you may use on disaster day to make sure you can meet your RTO. Remember, disaster recovery tests are not disruptive to your environment, and can be run scheduled or on demand.
Recovery Locations and the Readiness Check
Both storage recovery locations and restore recovery locations are checked during a readiness check. Orchestrator is looking for any obvious issues that would impede your recovery.
One of my favorite examples when I was setting up a new storage environment, I had my destination storage right, and I forgot to set an export policy. When I ran my readiness check, orchestrator let me know that those vSphere hosts were not able to see that storage and orchestrator as that as a problem. Likewise, it’ll look at the general health of your biosphere environment.
Another example is that if the recovery location has a host in maintenance mode, orchestrator is nice enough to let you know that hey, you have a host in maintenance mode, this might impact your ability to recover.
Once again, orchestrator will flag that for a closer look. Beyond the recovery locations, Orchestrator always checks if we can meet our RPO for each and every type of plan.
One thing I have noticed is that many people don’t bother monitoring their disaster recovery locations, so they won’t even notice when something has happened that could impact recovery. Orchestrator helps solve this problem with this lightweight check that will discover many issues. Of course the readiness check document can automatically be e-mailed to key stakeholders every time it runs.

Melissa is an Independent Technology Analyst & Content Creator, focused on IT infrastructure and information security. She is a VMware Certified Design Expert (VCDX-236) and has spent her career focused on the full IT infrastructure stack.